
© Railway Wonders of the World 2012-


The Shay Geared Locomotive
The development of the engine known as “the hill climber”
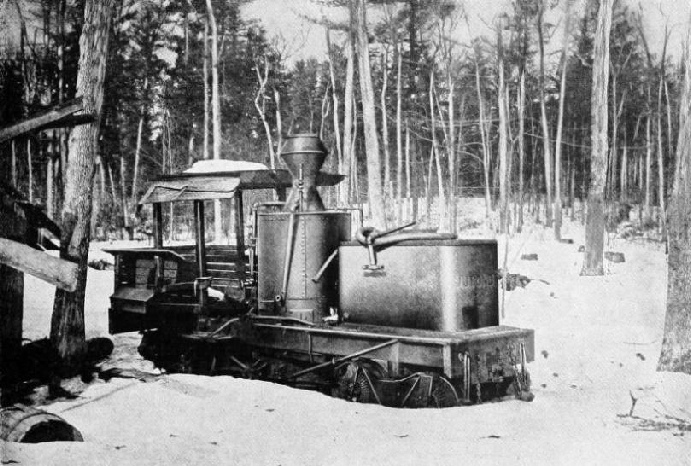
THE “M. J. BOND”, one of the earliest geared locomotives built by Mr. Ephraim Shay for logging in Michigan.
IN 1873 an enterprising American lumber magnate, Mr. Ephraim Shay, owned and operated an extensive saw-
The greatest difficulty was the transportation of the logs from the forests to the mill. Lumbering being essentially a winter calling, it is obvious that advantage must be taken of every minute of time. But the impassibility of the roads owing to snow and ice constituted a serious obstacle. Mr. Shay followed the conventional methods of logging by means of wheels and horses and encountered the general run of aggravating delays and difficulties, while the lumber was proving somewhat costly to bring down.
Under these circumstances he was forced to reflect whether a simpler, more expeditious, and cheaper system of haulage could not be introduced. The railway and the steam locomotive offered an obvious alternative, but he recognised that the conditions were adverse to its utilisation. Circumstances demanded a permanent way of the cheapest possible construction, comprising virtually the laying of the pair of rails upon the ground surface, ignoring banks and curves. There was another factor which had to be borne in mind. The rails would have to be moved time after time to tap the points where the lumber-
Thereupon the ingenious saw-
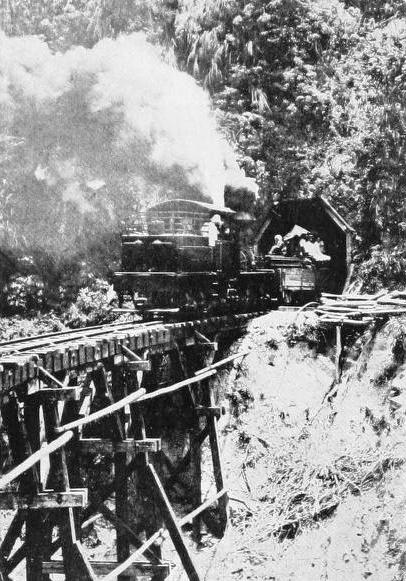

“THE HILL CLIMBER” ASCENDING A RISE OF 1 IN 20 ON THE MOUNT ARISAN LOGGING RAILWAY IN FORMOSA.
He set to work to build a locomotive according to the ideas he had evolved. The materials and facilities at his command in the backwoods were severely limited, but this fact did not deter him. He contrived some rails from maple wood, and laid them on rough sleepers fashioned from waste parts of the logs. He used the standard gauge because he bought some flat deck cars for his experiments, and they were built to this gauge. His locomotive was extremely crude. It comprised a vertical boiler which he placed upon a double truck flat deck car. At one end of the vehicle he placed his water-
Such was the first Shay geared locomotive. Its creator became the butt of ridicule among the camps for his pains. The locomotive certainly was a quaint-
So it did, and to such advantage that those who had hailed its appearance with laughter began to regard the experiment with serious interest. Directly the locomotive got out upon the road all sorts of troubles asserted themselves, but as they developed its designer attacked and remedied them. The result was that at last he got it to work pretty smoothly, and evinced the greatest pride in the fruits of his labour, because he was able to haul his logs quicker, more continuously, and cheaper by this means than were his rivals with their horses.
As this was the object for which he had striven he became completely satisfied with what he had accomplished. He proved that his locomotive could run and keep the track where an ordinary engine would fail completely. So he built additional improved engines, and in a short space of Ephraim Shay’s gear-
Luckily he was a very shrewd man business. The gibes of his competitors did not dissuade him from protecting the salient points of his ideas by means of Patent Acts. Then inquiries began to roll in from other sources. Contractors who appreciated the advantages of mechanical haulage, but who were faced with similar conditions concerning primitiveness of track, banks and curves, having heard of the achievements of the Shay geared engine, wanted them for their works.
The designer not being able to meet these demands by his own efforts, transferred his patents to two concerns, the Carnes Agerter Company and the Lima Locomotive and Machine Company, since amalgamated and now known as the Lima Locomotive Corporation, of Lima, Ohio. The invention, now placed in the hands of experienced and expert engineers, was developed very rapidly along approved locomotive lines.
Colloquially it has become known as “The Hill Climber”, and the nickname is appropriate. Its range of workability is wide both as regards gradients and curvature. It will climb banks ranging from 1 in 33 to 1 in 7, and will negotiate curves of 50 to 100 feet radius, conditions which it is safe to assert could not be fulfilled by many other types of locomotives with ease.
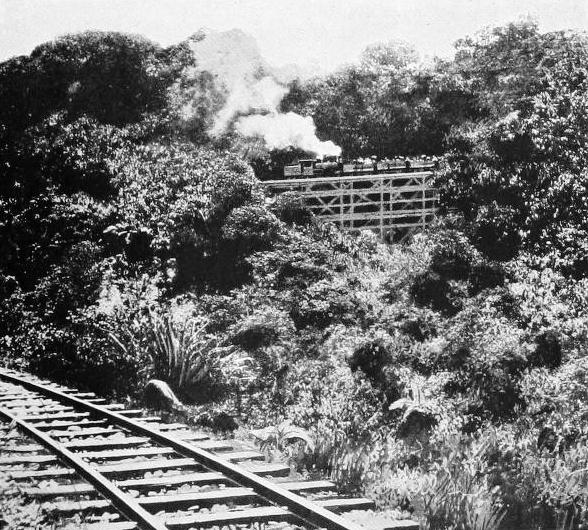

SHAY GEARED LOCOMOTIVE ROUNDING HORSE-
Although originally designed for service in lumber camps and upon contractors’ works, it has passed to other more useful spheres. Being built in all sizes from 10 to 160 tons weight, it is equally applicable to trunk line working where stiff banks and sharp curves abound. True, its speed capacity is limited, but that is a secondary consideration so long as it moves the loads imposed to and from the points required.
Its salient peculiarity is the enormous power developed at slow speed, and its extreme flexibility in negotiating the sharpest curves. On the Mount Arisan Railway in Formosa the banks run up to a maximum of 1 in 20, while the sharpest curves are only of 164 feet radius. Another interesting application is that upon the Mount Tamalpais Railway in California, where the heavy grades and sharp bends of this sight-
The modern expression of the Shay geared locomotive differs very radically from its original prototype although the fund-

THE LARGEST AND MOST POWERFUL SHAY GEARED LOCOMOTIVE IN SERVICE. In running order it weighs 160 tons, develops a tractive effort of 74,400 pounds, and hauls a load of 200 tons up a bank of 1 in 14·28.
When the Wolgan Valley Railway was carried some 30½ miles inland from Newnes Junction, on the New South Wales Government system, in order to tap the shale oil fields, the fact that some 1,760 feet difference in altitude had to be overcome in this distance offered a somewhat perplexing problem to the surveyors. The location gave banks of 1 in 22, and curves of 330 feet radius, which could not be eased owing to the configuration of the country. The operation of such a railway also occasioned considerable anxiety, as ordinary adhesion working was quite out of the question. The issue was closely investigated and after examining the Mount Tamalpais Railway and its Shay locomotives, which have to run over similar grades, and where the curves range between 70 and 80 feet radius, and also the Canadian Pacific Railway, where the Shay geared locomotives have to overcome curves of 230 feet radius, this system was adopted. In one particular case where Shay locomotives are at work it was found that whereas the maximum load capable of being hauled by the geared engine was 5,781 tons on the level, it could pull 1,556 tons up a bank of 1 in 100, 852 tons up 1 in 50, 484 tons up 1 in 25, and 235 tons up 1 in 16·66. The latter grade is quite impossible to ordinary adhesion working. The only alternative to the Shay geared locomotive was the rack system or the Fell centre rail such as worked the mail traffic over Mont Cenis during the boring of the tunnel. Seeing that the conditions fulfilled in this instance were closely allied to those which had to be faced in Australia, twp 70-
In the country of its origin the Shay geared locomotive has been adopted extensively and many striking machines of this type have been built. The latest and most remarkable is that designed for the Kansas City Southern Railway in connection with the operation of the new terminals of this system which have been completed on the north side of Kansas City, Missouri. This is the largest and most powerful geared locomotive in operation in the world to-
The duty which this engine has to fulfil is of a very exacting character, and demonstrates very conclusively the enormous power developed by this geared system. Owing to every wheel being a driver and available for adhesion the locomotive is able to develop a tractive effort of 74,400 pounds. It was designed to haul a train load of 200 tons up a grade of 1 in 14·28 on which there are some sharp curves, and upon reaching the top of the bank to negotiate curves of 95·5 feet radius in order to move the cars to and from the various warehouses.
Despite the fact that this huge geared locomotive was built 30 years after the inventor, Mr. Ephraim Shay, contrived his first crude engine to facilitate his logging operations, strict adherence has been made to the original Shay idea -
cylinders are placed on the side, and are geared with each wheel by a flexible shaft, so that each wheel becomes a driver, and all the weight of the locomotive and tender is disposed over the driving wheels. Since Mr. Shay evolved his unique solution for overcoming an exasperating difficulty in the backwoods of Michigan several different types of geared loco-
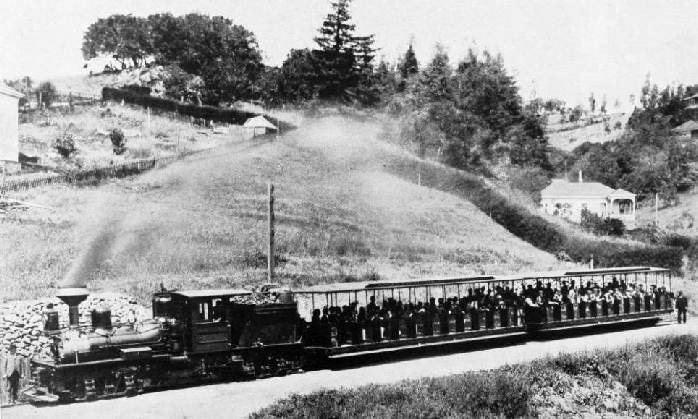

THE SHAY GEARED LOCOMOTIVE AT WORK UPON THE MOUNT TAMALPAIS RAILWAY IN CALIFORNIA.
[From Part 19 of Railway Wonders of the World by Frederick A. Talbot]
You can read more on “The Mount Tamalpais Railway”, “Rack Rail Locomotives” and “Unconventional Locomotives” on this website.