
© Railway Wonders of the World 2012-


London’s First Railways
The Forerunners of a Vast Network
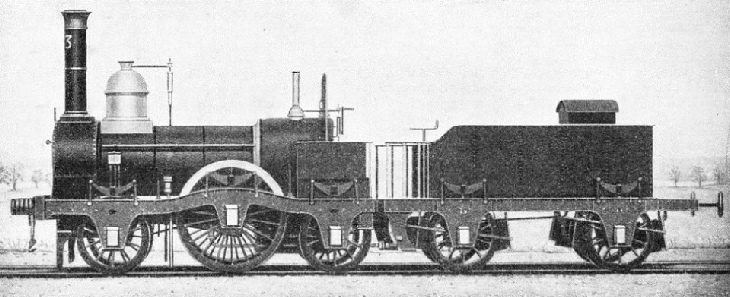
AN EARLY LOCOMOTIVE, which ran on London’s first railway from London to Greenwich. Built for the South Eastern Railway, the overall length of the engine and tender was 36 ft 4-
IT was not until 1836 -
There had, however, been earlier attempts to run a railway of one kind or another. Trevithick had, in 1808, operated one over a circular track forming part of the site of the present Euston Station. A public railway on which traction was by horses had also been opened for traffic in the Metropolitan area as early as 1803.
This pioneer, the “Grand Surrey Iron Railway”, took the place of a scheme to construct a canal between Wandsworth and Croydon. The River Wandle was then the busiest river of its size in Europe. There were nearly forty factories and mills on its banks, giving employment to three thousand people.
But the scheme to make a canal from Wandsworth to Croydon interfered with vested interests, and it was abandoned. The plan for a railway took its place.
The promoters lost no time, and on May 21, 1801, the Royal Assent (the first of its kind, since Parliamentary sanction was not needed for the early colliery railways in the north of England) was given to the Company’s Act. From the beginning, it was planned as a public railway -
The original scheme provided for a line from Croydon to Wandsworth, with short spurs to various factories on the route, and a branch to Hackbridge, Surrey. It was opened for traffic on July 26, 1803, and cost about £7,000 a mile. The original capital was £55,000. The track was composed of plate rails with inner and outer flanges, supported on stone sleepers.
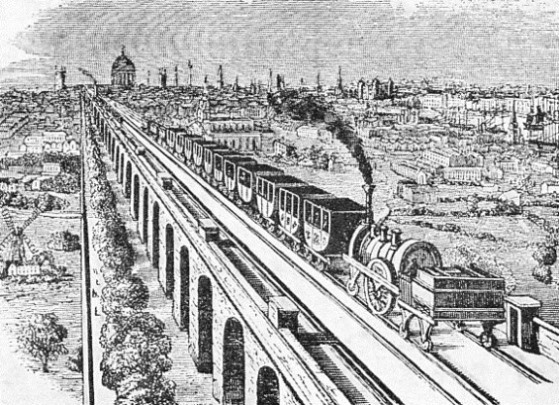
THE GREENWICH RAILWAY IN 1837. The railway approached the capital along a viaduct 3¾ miles long. This viaduct consisted of 878 brick arches. These were mostly of 18 ft span, and 22 ft high. The Greenwich Railway was opened for traffic in 1836.
Although the whole of the track has long since disappeared, the line at the time was regarded as so successful that a new company obtained an Act of Parliament in 1803 to extend the system to Godstone, via Merstham, and also to build a branch to Reigate. This undertaking, however, stopped at Merstham, mainly because the construction costs were considerably in excess of the estimates, and the whole of the “vast and important undertaking”, as it was called in a contemporary account, was acquired by the London, Brighton and South Coast Railway under its Act of 1837. Traffic on the section between Wandsworth and Croydon ceased on August 31, 1846, and the last of the track was taken up in 1848.
The First Signal Box in the World
On the other hand, the London and Greenwich is still an important link in the main English system. This line was planned in 1832 and secured its Act of Parliament in the following year, when the public was asked to subscribe £400,000 in £20 shares. Construction began in 1834. The initial section was carried on arches; despite the wintry weather and heavy gales, nearly 500 arches had been built by July, 1835. On January 19, 1836, notwithstanding the collapse of two arches the previous day, two special trains, “conveying Cambridge scientists”, were run between Spa Road and Deptford.
The public opening of this section took place on February 8, and it is on record that the receipts for the first week were £17, and for the second £31. Part of this money was derived from the public, who walked along the line on Sundays, when -
The first engines were of the 2-
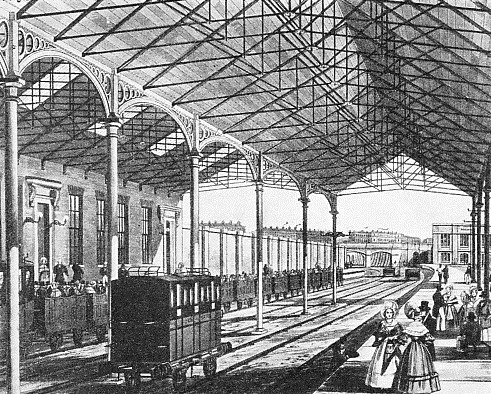
EUSTON STATION IN 1837. The station at Euston Square was then the London terminus of the London and Birmingham Railroad. This was the second railway to come to London.
Apart from being the first steam-
But for the conservatism of the London and Birmingham directors, the line would have been the first to make regular use of the electric telegraph. As early as 1837 Cooke and Wheatstone had made successful experiments between Euston and Camden with this means of communication. The directors refused to allow them to extend the system, and the inventors brought the idea to the Great Western, which adopted the device, and installed it between Paddington and West Drayton, Middlesex, in 1839. By 1843, the wires reached as far as Slough. Two years later the installation was instrumental in securing the arrest at Paddington of John Tawell, who had committed a murder near Slough in Buckinghamshire. He had escaped on the next train, only to be met by the police on his arrival at London. This is one of the first, if not the first, recorded instances of the use of the telegraph in capturing a criminal.
London was definitely placed on the railway map in 1838, since in addition to the completion of the London and Birmingham, the first sections of the London and Southampton (later London and South Western) and of the Great Western were opened. Traffic on the former system began in May between Nine Elms, Wandsworth, and Woking, Surrey. The extension to Waterloo was not brought into use until 1848. This is one of the few instances in which the original London terminus of a main line afterwards became its goods station. Bricklayers’ Arms is another. For many years Nine Elms was the site of the South Western’s locomotive shops, but these were eventually transferred to Eastleigh, near Southampton.
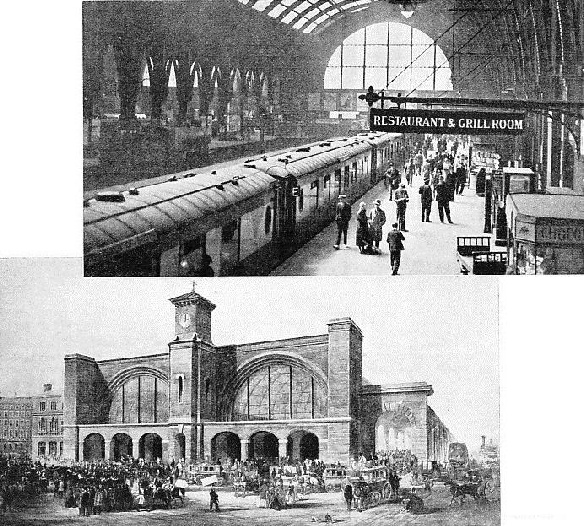 KING’S CROSS TO-
KING’S CROSS TO-
KING’S CROSS YESTERDAY provides a striking contrast to the illustration above. The scene shows the opening of the terminus of the Great Northern in 1852. The Great Northern Railway was merged with the LNER in 1923.
The scheme for a combined terminus at Euston -
With the exception of Waterloo and London Bridge (Brighton section), all the London termini were north of the river. Owing to the engineering difficulties involved in bridging the Thames, many of the stations were not finished until years after the railways by which they were owned had entered London. These delays may serve to explain, at least in part, why the scheme for a central union station, so common in the United States, never came to fruition. It is true that both Victoria and London Bridge served two companies prior to grouping, but each had its own approach lines, so that Victoria was in fact two stations, while London Bridge, including the low-
Some of the best known London stations were opened at a much later date than is realized by the majority of the passengers who use them regularly. Thus, while Bricklayers’ Arms was inaugurated as the South Eastern’s “West End passenger station” as early as 1844, Charing Cross was not opened until twenty years later, four years before Victoria. The latter was originally provided with both broad and narrow gauge tracks, since the Great Western was a joint owner of the property, and used the station as a southern suburban terminus. The South Eastern’s Cannon Street followed in 1866; and Holborn Viaduct, owned by the rival London, Chatham and Dover, was not available before 1874; and St. Paul’s not until ten years later.
Largest Suburban System
It has often been asked why the Brighton, Chatham, and South Eastern should have required so many termini, when the South Western, which was much the largest undertaking of the four, contented itself with one. The answer lies partly in the long rivalry between the South Eastern and Chatham, which for duration and intensity has never been surpassed in the history of our railways. The answer is also in the undeveloped condition of road transport in the early days of railways; and in the fact that at the beginning of the railway era South London was so much more thickly populated than the north and west that suburban traffic on a large scale first originated from and to the districts south of the Thames. To this day the Southern’s suburban network is far more considerable than that of any of the other railway groups, and the geographical lay-
The second main line from the north to reach London was the Great Northern, whose King’s Cross Station was opened to traffic in October 1852. Like its near neighbour, St. Pancras, the terminus was originally built with a single-
St. Pancras itself was relatively late in materializing. The Midland had reached London by February 1, 1858, but the whole of the journey was not over its own metals, which terminated at Hitchin, Herts, whence the trains ran over the Great Northern’s lines to King’s Cross. St. Pancras was not opened until October 1868. The need for the company to possess a station of its own had become urgent long before then. It is recorded that in 1862 nearly 3,500 trains suffered more or less serious delay on the short section between Hitchin and King’s Cross; and since this naturally affected the trains of the Great Northern, the latter company gave the Midland notice to quit its temporary terminus at the King’s Cross coal depot. St. Pancras itself incidentally serves as the top floor of the largest beer barrel warehouse in the world, the passenger station forming the roof of the warehouse.
Early Electricity
Just as the Great Northern had given hospitality to the Midland, so was St. Pancras at first used as one of the terminals of the Great Eastern Railway. This line, which was originally laid on the 5 ft gauge and converted to standard in 1845, did not open Liverpool Street Station until February 1874, but trains began to run into St. Pancras in July 1870. Up to 1874 the principal Great Eastern terminus was at Shoreditch, half a mile out of Liverpool Street, now a large and busy goods depot.
The ramifications of the London Underground system that grew out of the Metropolitan’s short parent stem from Paddington to Farringdon Street have already been dealt with on another page. But it may be mentioned here that the Metropolitan and its associate the Metropolitan District have other claims to distinction besides inaugurating underground travel. They were the first to build a circle railway, a lay-
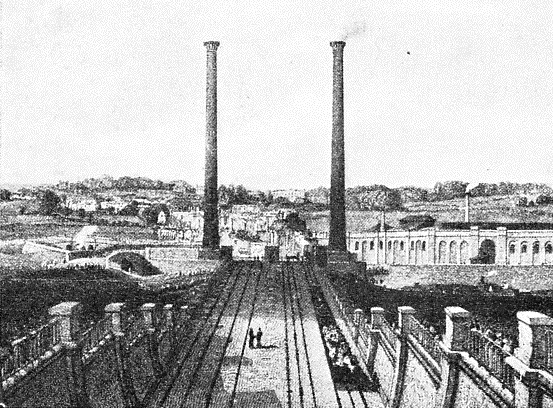
THE APPROACH TO EUSTON STATION IN 1837. Trains were originally worked down the incline by gravity, and when leaving Euston they were hauled up by stationary engines and endless ropes, two and a half miles long, each costing £460.
The immense expansion both in the size and population of London since the second half of last century has been due partly to this underground network, of which there are to-
The population of Hendon, which was only 29,000 in 1907, when the Hampstead Tube did not extend beyond Golders Green, had risen to 116,000 when the last census was taken.
The year 1840 saw the opening of the London and Blackwall Railway, which was originally built on the 5 ft gauge and used cable traction. This method was decided on because the line ran through densely populated areas, and it was thought that locomotives would be too dangerous, owing to the “burning coke flying about among the roofs of the contiguous houses”.
The ropes, which weighed about forty tons each, and were called on to travel over 300 miles a day, were worked by stationary steam engines of marine pattern. On this line as many as 101 trains were operated a day.

THE IMPOSING ENTRANCE TO EUSTON as it appeared when the station was the terminus of the London and Birmingham Railway. A scheme to make the station the joint terminus of the London and Birmingham and Great Western Railways failed to materialize.
WATFORD TUNNEL as it was when the London and Birmingham Railway first gained access to London. The tunnel was built to avoid spoiling the estates of two powerful landlords who opposed the railway's passage across their property. The original survey was carried out by Robert Stephenson, the son of the famous George Stephenson.
PADDINGTON IN 1862 from a famous painting by W. P. Frith, RA, The Great Western’s terminus was designed by the Company’s engineer, Isambard Brunel. The station replaced the original in 1854, the reconstruction costing £534,000. The interior of the principal part of this station when completed was 700 ft long and 238 ft wide.
You can read more on “The Atmospheric Railway”, “The Story of the Locomotive”,
“When Railways Were New” and “The World’s Most Famous Railway” on this website.